In the world of auto repair and home maintenance, a "glass fixer" plays a crucial role. This tool is designed to address issues with cracked or damaged glass, especially in vehicles. Instead of replacing entire windshields, using a glass fixer can save time and money. It often involves resin and a pressure system to fill cracks, restoring structural integrity.
Understanding how a glass fixer works can be fascinating. When applied correctly, the resin seeps into cracks, hardening to create a strong bond. The process seems straightforward, yet small mistakes can lead to ineffective results. It's important to follow instructions carefully. Sometimes, users may rush the application, resulting in visible imperfections.
Learning about glass fixers unveils a combination of science and practicality. While this tool offers convenience, the skill lies in its application. Reflecting on its effectiveness invites curiosity about refining techniques. A glass fixer serves as a reminder that mastering any tool requires patience and practice.


A glass fixer is a professional who specializes in repairing broken or damaged glass pieces. This can include windows, mirrors, or even glass furniture. The process requires specific skills and tools to ensure the glass is restored effectively. According to industry reports, the glass repair market is expected to grow significantly, driven by increased demand for sustainable repair options.
Glass fixers use a variety of techniques to mend glass. Adhesives are commonly used for smaller cracks. In more extensive damages, replacement of the glass segment might be necessary. The choice of method depends on the type of glass and the extent of damage. A skilled fixer can often restore the clarity and strength of the original material. However, results vary. Not every repair is perfect. Some repairs may leave noticeable marks, and reflection might be altered.
**Tips:** Always choose a fixer with proper credentials. Check reviews and previous work examples. For minor repairs, consider DIY kits available in stores. They can be simple. Yet, remember that mistakes are easy to make. Consulting a professional can save you from costly errors.
A glass fixer system typically consists of several essential components. These include a heated glass surface, emission sensors, and control software. The heated surface plays a crucial role in the quick elimination of moisture. This element is vital, especially in colder climates, where condensation can be a persistent issue. Studies indicate that proper heating can reduce fogging by nearly 80%, enhancing visibility.
Emission sensors are another critical component. They monitor the glass's temperature and environmental conditions. However, these sensors can sometimes falter, leading to inefficient operations. It's essential to regularly calibrate and test them. Industry reports suggest that over 40% of glass fixer systems lose efficiency due to sensor malfunctions. This statistic highlights the need for routine maintenance and checks.
Control software integrates the entire system. It analyzes data from the sensors and adjusts settings accordingly. Yet, this software can be complex. Users may struggle with its interface, especially in urgent situations. Moreover, if the data input is wrong, the system might not perform optimally. This nuance points to an ongoing challenge in ensuring user training and system reliability.
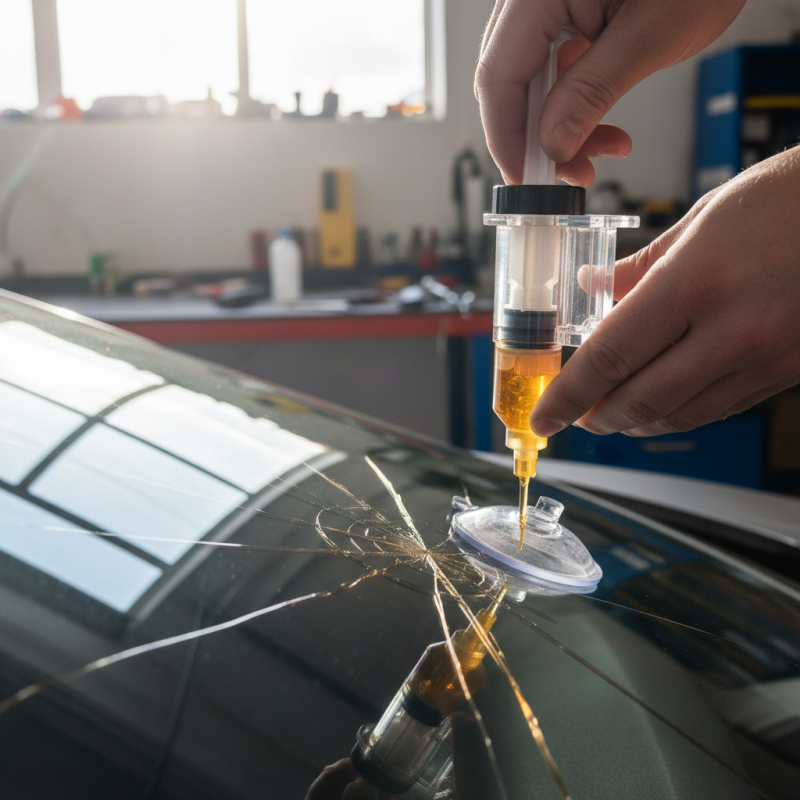
Glass fixers are essential for maintaining the integrity of glass surfaces. The process starts with assessing the damage. Small cracks or chips can often be repaired. Larger damage may require replacement. Before proceeding, glass fixers clean the area thoroughly. This ensures proper adhesion of the repair material.
After cleaning, an injectable resin is used. The resin penetrates cracks, bonding the glass together. It cures under UV light, forming a strong bond. Reports indicate that effective repairs can restore up to 80% of the glass's original strength. Glass fixers often use specialized tools for precision. This enhances the quality of the repair and reduces imperfections.
Tips: Always consider the weather. Temperature and humidity can affect the curing process. Also, evaluate the glass's condition. Sometimes, replacement is more cost-effective. Regular maintenance checks can prevent severe damage. Waiting too long to fix minor issues can lead to bigger problems.
Glass fixers are essential tools in the construction and repair industries, with various common applications. They are primarily used for bonding, sealing, and fixing glass panels in structures like windows and doors. According to a recent report from MarketsandMarkets, the global glass adhesive market is projected to reach over $3.9 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing reliance on effective glass fixers.
In residential settings, glass fixers are often used for installing shower doors and mirrors. Proper installation is crucial. Any tiny misalignment can lead to leaks or breakage. In commercial spaces, they are employed for glass storefronts and facades. The aesthetic appeal directly impacts customer perception. A well-fixed glass can enhance visibility and attract more foot traffic.
Tip: Always ensure the surface is clean and dry before applying a glass fixer. This simple step can significantly improve adhesion. Regular maintenance checks are also advisable. Small cracks or imperfections can compromise the entire structure over time.
In some cases, glass fixers may not perform as expected. Factors like humidity and temperature can affect curing times. It's vital to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines. Remember, a small oversight during application can lead to larger issues later on.
| Application | Function | Advantages | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Windows | Repairing or replacing damaged panes | Cost-effective solution, improved insulation | Tempered glass, double-pane glass |
| Automotive | Fixing windshields and side windows | Enhances safety, quick repairs | Laminated glass, tempered glass |
| Commercial Buildings | Replacing or repairing storefront glass | Improves aesthetics, increases security | Annealed glass, safety glass |
| Shower Enclosures | Installing or fixing glass panels | Customizable designs, water resistance | Tempered glass, frosted glass |
| Mirrors | Repairing or replacing damaged mirrors | Enhances lighting, aesthetic appeal | Silvered glass, acrylic mirror |

A glass fixer is a tool used to repair damaged glass surfaces. It offers significant advantages across various industries. In construction, it can restore broken window panes quickly. This minimizes downtime and enhances worker safety. In the automotive sector, glass fixers help repair windshields efficiently, saving time and costs.
When thinking about using a glass fixer, consider these tips. Make sure the surface is clean and dry before applying any product. This ensures better adhesion and results. Another point to remember is to read the instructions carefully. Each setup may vary slightly, affecting the outcome.
In the electronics industry, glass fixers play a crucial role. They quickly fix screens on devices. This reduces waste and improves product lifespan. However, it’s essential to note that some repairs may not be perfect. Always review the finished work closely. Sometimes, a second pass is necessary to achieve desired results.