nail intramedullari is a significant innovation in orthopedic surgery. It plays a crucial role in treating fractures, particularly long bone injuries. According to industry reports, the global intramedullary nail market reached $2.5 billion in 2022. It is projected to grow steadily at a CAGR of 5.8% through 2030.
The use of Nail Intramedullari provides enhanced stability and mobility for patients. Surgeons often prefer it for its minimally invasive nature. However, complications can arise. Infection and improper alignment are notable concerns. Surgeons must evaluate each case critically.
Despite its advantages, many practitioners face challenges. Training and experience vary significantly among surgeons. This inconsistency impacts patient outcomes. Continuous education and hands-on practice are vital for mastery. Recognizing these gaps will help improve overall effectiveness in using Nail Intramedullari. The focus should remain on refining techniques and optimizing patient care.
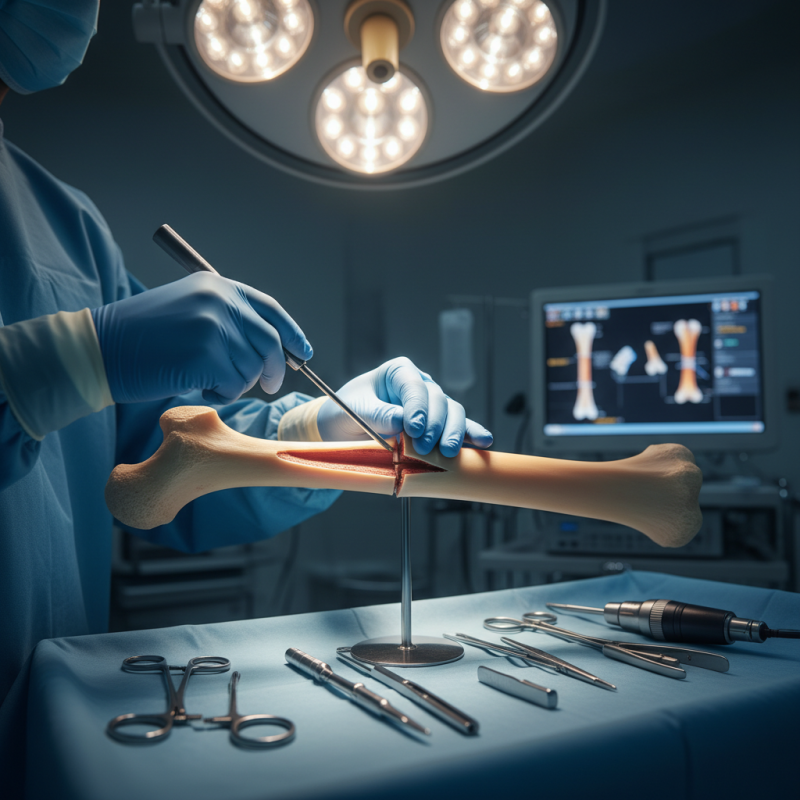
Nail intramedullari is a surgical technique used for managing fractures, particularly in long bones like the femur and tibia. It involves inserting a metal rod inside the hollow cavity of the bone. This method provides stability and promotes healing without extensive external support. Surgeons often prefer this because it allows for better alignment of the bones.
During the procedure, a small incision is made at the site of the fracture. The intramedullary nail is then carefully inserted. This can be quite tricky. Proper placement is critical, and misalignment can lead to complications. Pain and rehabilitation are significant factors to consider. Some patients experience discomfort during recovery. Each case is unique, and outcomes can vary.
The advantages of nail intramedullari include reduced recovery time and increased mobility. However, there are risks. Infection, nerve damage, and improper healing are possible concerns. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential. Understanding both risks and benefits can help patients make informed decisions. Clear communication with doctors can also ease anxiety about the procedure.
Intramedullary nail technology has evolved significantly since its inception. Initially introduced in the mid-20th century, this technique revolutionized the treatment of long bone fractures. Early pioneers focused on maximizing stability while minimizing complications. According to a study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, intramedullary nails have shown an impressive union rate of approximately 90% for femoral fractures.
Despite these advancements, challenges remain. Surgeons often face issues like malalignment or infection. A report from the American Journal of Orthopedics indicated that nearly 15% of patients may experience complications related to intramedullary nailing. This highlights the need for ongoing research and technical refinement in the field.
Tips for successful outcomes include proper surgical technique and patient selection. Understanding the unique anatomy of each patient can enhance the chances of favorable results. Additionally, communication within the surgical team is crucial to minimize errors during the procedure. Continuous education and awareness of new techniques can further improve patient outcomes. Consideration of these factors can create a more effective approach to intramedullary nailing.
| Year | Event | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | Introduction of Intramedullary Nailing | Revolutionized fracture fixation methods. |
| 1980 | Development of Interlocking Nails | Increased stability and reduced complications. |
| 1990 | Introduction of Locking Mechanisms | Enhanced control over fracture alignment. |
| 2000 | Advancements in Biomechanics | Improved design for better load distribution. |
| 2020 | Use of Biodegradable Materials | Potential for reducing revision surgeries. |
Intramedullary nails have become a crucial tool in orthopedic surgery. Surgeons use them for various indications. One common reason for using these nails is to treat long bone fractures. They are especially effective for fractures in femurs and tibias. The nail is inserted into the medullary cavity, providing support and stability during healing.
Another important indication for intramedullary nails is the treatment of osteotomy. This procedure, often used to correct deformities, benefits from the nail's alignment capabilities. It helps maintain proper bone positioning during recovery. Additionally, these nails can be important in cases of complex fractures, where traditional casting may not suffice. Intramedullary nails provide a more secure method to manage these challenging injuries.
Despite their advantages, the use of intramedullary nails has some complexities. The insertion can sometimes lead to complications. These may include infection or improper alignment. Surgeons must carefully weigh the benefits against potential risks. Each case requires thorough assessment and planning. Understanding these factors is essential for successful outcomes in orthopedic surgery.
Intramedullary nails are a key tool in orthopedic surgery for stabilizing bone fractures. They are inserted into the marrow canal of a long bone, providing internal support. This method allows for immediate weight-bearing. Studies suggest that 85% of patients experience satisfactory outcomes with this technique.
The mechanism of action for intramedullary nails is interesting. The nail’s design and placement create a tension mechanism that supports healing. The intramedullary nail transfers loads from the fracture site to the more stable areas of the bone. This process encourages quicker union. According to recent data, healing rates can reach up to 94% with proper alignment and placement.
However, there are challenges. Surgeons may encounter complications such as infection or improper alignment. One report indicates that 10-15% of patients face issues post-surgery. These factors highlight the importance of careful planning and technique. Effective use of intramedullary nails requires ongoing training and skill enhancement for orthopedic specialists.
Nail intramedullari surgery is a common procedure for treating long bone fractures. However, it comes with various complications and risks that patients should consider. According to a study published in the Journal of Orthopedic Surgery, around 10% of patients experience complications post-surgery. These can include infections, malunion, or nonunion of the bone. In rare cases, nerve or blood vessel damage may also occur.
Infection is one of the most significant risks associated with this surgery. A local infection can lead to further complications, which may require additional interventions. Studies have shown that the risk of infection increases with the patient's age and underlying health conditions. Patients should be proactive about discussing their medical history with their surgeons to mitigate these risks.
Tips: Follow post-operative care instructions carefully. Maintain a clean surgical site to prevent infection. Awareness of warning signs, such as increased pain or swelling, is crucial. Some patients may find it challenging to stick to their rehabilitation plan, leading to slower recovery. Consider regular check-ins with healthcare providers to stay on track.